Alan Turing
The Life and Achievements of Alan Turing
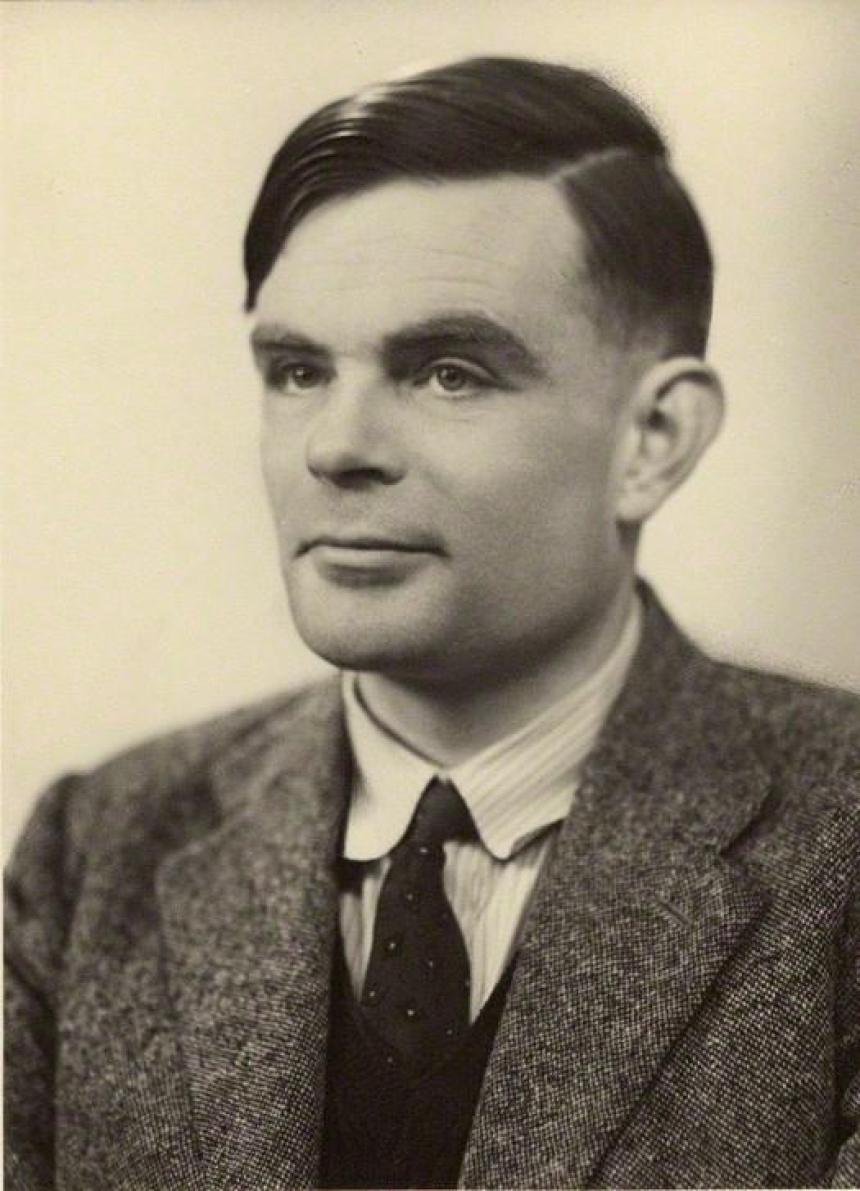
The Life and Achievements of Alan TuringAlan Turing was a British mathematician, logician, and computer scientist who made significant contributions to the fields of mathematics, cryptography, and computer science. Born on June 23, 1912, in London, Turing showed great potential from an early age. He attended Sherborne School and later studied mathematics at King's College, Cambridge, where he graduated with first-class honors in 1934.
Early Work and CryptographyAfter completing his studies, Turing began working at the Government Code and Cypher School (GC&CS) in Bletchley Park, where he played a crucial role in breaking German ciphers during World War II. Turing's work involved developing machines that could decrypt German messages, including the famous Enigma machine. His innovations in cryptography were groundbreaking and contributed greatly to the Allied forces' ability to gather intelligence and turn the tide of the war.
The Turing Machine and ComputabilityOne of Turing's most significant contributions to the field of computer science was the development of the Turing machine. This hypothetical device, devised in 1936, served as a foundation for modern computing. The Turing machine consists of an infinite tape divided into squares, a read/write head, and a set of instructions. It was designed to simulate any algorithmic computation and laid the groundwork for the development of digital computers.
Turing's work on computability also led to the concept of the Turing test, a way to measure a machine's ability to exhibit human-like intelligence. The Turing test remains an essential benchmark in the field of artificial intelligence.
Post-War and Tragic EndAfter the war, Turing continued his work in the emerging field of computer science. He worked at the National Physical Laboratory, where he contributed to the development of early computer designs. Turing's visionary ideas and insights into computing were ahead of their time.
However, in 1952, Turing's life took a tragic turn when he was prosecuted for homosexual acts, which were criminal offenses in the UK at the time. To avoid imprisonment, Turing underwent chemical castration as an alternative to a prison sentence. The treatment affected his physical and mental well-being, and he tragically died by suicide on June 7, 1954.
Legacy and RecognitionDespite the tragic end to his life, Turing's contributions to the fields of mathematics, cryptography, and computer science have earned him widespread recognition and admiration. His work paved the way for modern computing and his ideas continue to shape the field today.
In 2013, Turing was posthumously pardoned by Queen Elizabeth II for his conviction of "gross indecency." This pardon, along with other posthumous honors, including the Turing Awardóconsidered the Nobel Prize of computer scienceóhave helped bring awareness to Turing's remarkable achievements and the unjust treatment he faced.
ConclusionAlan Turing was a brilliant mathematician and computer scientist whose groundbreaking work revolutionized the fields of cryptography and computer science. His contributions continue to impact our lives today, shaping the way we understand and utilize technology. Despite facing adversity in his personal life, Turing's legacy remains an inspiration for future generations of mathematicians, scientists, and computer experts.
Frequently Asked Questions1. What is the Turing machine?
The Turing machine is a hypothetical device that was developed by Alan Turing in 1936. It served as a foundation for modern computing, simulating any algorithmic computation.
2. What is the Turing test?
The Turing test is a measure of a machine's ability to exhibit human-like intelligence. It is used to determine if a machine can successfully imitate human conversation.
3. What were Turing's contributions to cryptography?
Turing's work during World War II involved breaking German ciphers, including the Enigma machine. His innovations in cryptography greatly aided the Allied forces in gathering intelligence.
4. Why was Alan Turing persecuted?
Turing was persecuted for homosexual acts, which were considered criminal offenses in the UK at the time. He was chemically castrated as an alternative to imprisonment.
5. How is Alan Turing remembered today?
Turing's remarkable achievements have earned him widespread recognition and admiration. He is remembered as a pioneer in mathematics, cryptography, and computer science.