Antoine Lavoisier
The Life and Contributions of Antoine Lavoisier
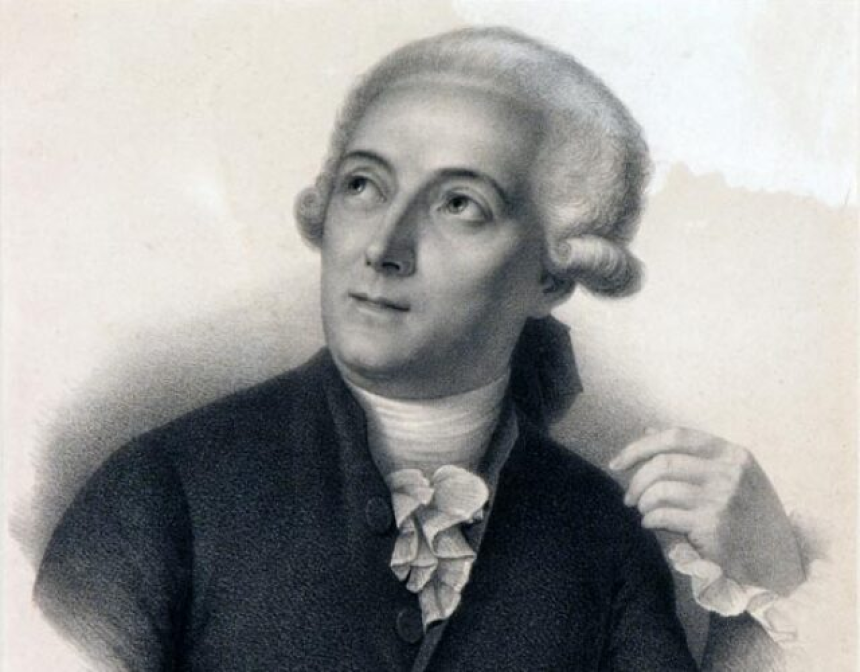
The Life and Contributions of Antoine LavoisierAntoine Lavoisier was a French chemist and nobleman who is often referred to as the "Father of Modern Chemistry." Born in Paris in 1743, he played a crucial role in the scientific revolution of the 18th century. Lavoisier's groundbreaking work laid the foundation for our understanding of chemical elements and their reactions. His experiments, theories, and meticulous attention to detail revolutionized the field of chemistry as we know it today.
Lavoisier's most significant contribution to chemistry was his discovery and formulation of the law of conservation of mass. Through extensive experimentation, he demonstrated that during a chemical reaction, matter is neither created nor destroyed, but only transformed. This concept was a major departure from the prevailing theories of the time, which suggested the existence of "phlogiston" as a substance released during combustion. Lavoisier's experiments proved that the increase in weight during combustion was due to the combination of oxygen from the air with the substance being burned.
Apart from his work on the law of conservation of mass, Lavoisier also introduced the concept of chemical elements as fundamental units of matter. He compiled the first modern list of elements, identifying and naming 33 of them. Lavoisier disproved the ancient "Four Elements" theory (earth, water, air, and fire) and asserted that they were, in fact, compounds made up of different elements. Furthermore, he introduced a new system of chemical nomenclature based on his meticulous experiments and observations, which set the stage for the standardization of chemical terminology.
Lavoisier's research extended beyond theoretical chemistry. He was also instrumental in the development of new methods for analysis and measurement. He invented the chemical balance for accurate weighing and was the first to use it consistently in his experiments. Additionally, Lavoisier contributed to the understanding of gases, developing the concept of oxidation and coining the term "oxygen." His work on the composition of water, along with his wife Marie-Anne Lavoisier, led to a new understanding of its chemical composition.
Despite his significant contributions to science, Antoine Lavoisier's life came to a tragic end. During the French Revolution, he was falsely accused of selling watered-down tobacco to the government. Lavoisier, along with 27 other tax collectors, was sentenced to death by guillotine in 1794. His untimely death marked a great loss to the world of chemistry, but his legacy and contributions continue to inspire scientists to this day.
Frequently Asked Questions1. What were Antoine Lavoisier's major contributions to chemistry?Antoine Lavoisier made several major contributions to chemistry. He discovered the law of conservation of mass, introduced the concept of chemical elements, developed a new system of chemical nomenclature, and contributed to the understanding of gases and the composition of water.
2. How did Lavoisier revolutionize the understanding of chemical reactions?Lavoisier revolutionized the understanding of chemical reactions by disproving the prevailing theory of phlogiston and introducing the concept of the law of conservation of mass. His experiments showed that matter is neither created nor destroyed during a chemical reaction, but only transformed.
3. What is the law of conservation of mass?The law of conservation of mass, discovered by Antoine Lavoisier, states that in a chemical reaction, the total mass of the reactants is equal to the total mass of the products. Matter is neither created nor destroyed; it is only transformed.
4. How did Lavoisier contribute to the development of chemical analysis?Lavoisier contributed to the development of chemical analysis by inventing the chemical balance for accurate weighing and using it consistently in his experiments. His meticulous attention to detail and emphasis on precise measurement revolutionized the field of chemistry.
5. What was Antoine Lavoisier's fate during the French Revolution?During the French Revolution, Antoine Lavoisier was falsely accused of selling watered-down tobacco to the government. He, along with 27 other tax collectors, was sentenced to death by guillotine in 1794. His tragic death marked the end of a brilliant scientific career.