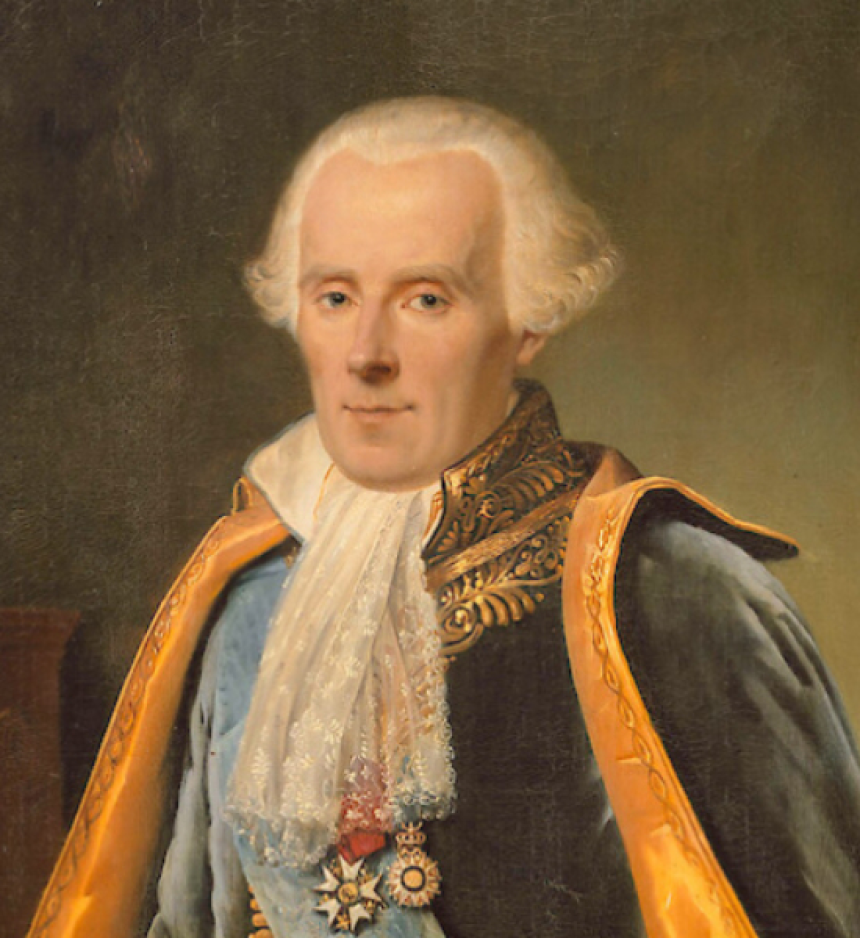
Pierre-Simon Laplace
Pierre-Simon Laplace: A Brilliant Mind in Mathematics
Pierre-Simon Laplace: A Brilliant Mind in MathematicsPierre-Simon Laplace, born on March 23, 1749, in Beaumont-en-Auge, France, was a renowned mathematician and astronomer who made significant contributions to both fields. His work had a profound impact on the scientific community, and his theories are still taught and studied today.
Early Life and EducationLaplace was born into a modest family, but his passion for learning was evident from a young age. He excelled in mathematics and quickly gained a reputation for his exceptional analytical skills. Laplace's talent did not go unnoticed, and he received a scholarship to attend the University of Caen to study mathematics and physics.
During his time at the university, Laplace immersed himself in his studies and made significant progress in various mathematical disciplines. He became particularly interested in celestial mechanics, inspired by the work of Isaac Newton. Laplace's brilliance and dedication to his studies soon caught the attention of prominent mathematicians and astronomers, allowing him to pursue an impressive career.
The Laplace's EquationOne of Laplace's most significant achievements is his contributions to the field of partial differential equations. He formulated the Laplace's equation, which describes the behavior of scalar fields in three dimensions. This equation has numerous applications in physics, engineering, and other sciences.
Laplace's equation is particularly important in electrostatics, fluid dynamics, and heat transfer. It provides a mathematical framework to solve problems involving the distribution of electric potentials, fluid flow, and temperature distribution. Laplace's equation forms the foundation for many advanced mathematical techniques used in these fields.
Celestial Mechanics and the Laplace DeterminantLaplace's contributions to celestial mechanics revolutionized our understanding of the solar system. He derived the Laplace determinant, a mathematical tool that allows the calculation of perturbations in planetary orbits. This discovery enabled scientists to accurately predict the positions of celestial bodies with unprecedented precision.
Furthermore, Laplace developed the theory of secular perturbations, which explains long-term changes in the orbits of planets caused by gravitational interactions. His work was instrumental in explaining irregularities in planetary motion, such as the precession of planetary orbits and the stability of the solar system.
Later Life and LegacyIn addition to his groundbreaking research, Laplace held various prestigious positions throughout his career. He served as the Minister of the Interior under Napoleon Bonaparte and was elected to the French Academy of Sciences. Laplace's work and contributions earned him numerous accolades, including the Copley Medal from the Royal Society of London.
Laplace's legacy extends far beyond his lifetime. His theories and discoveries continue to shape modern mathematics and physics. Many of his concepts and equations are still taught in classrooms worldwide. Laplace's influence can be seen in various fields, including mathematical physics, astronomy, and probability theory.
ConclusionPierre-Simon Laplace was a visionary mathematician and astronomer who left an indelible mark on the scientific community. His contributions to disciplines such as celestial mechanics and partial differential equations paved the way for new discoveries and advancements in various scientific fields. Today, Laplace is remembered as one of the greatest minds in the history of mathematics and astronomy.
Frequently Asked Questions1. What are some practical applications of Laplace's equation?
Laplace's equation is widely used in physics, engineering, and other scientific disciplines. Some practical applications include analyzing the flow of heat in solids, modeling fluid dynamics, and calculating electric potentials in conductors.
2. How did Laplace's work impact the understanding of planetary motion?
Laplace's contributions to celestial mechanics led to a better understanding of planetary motion and the stability of the solar system. His theories and equations allowed scientists to predict and explain the irregularities observed in the orbits of planets.
3. What is the Laplace determinant?
The Laplace determinant is a mathematical tool developed by Laplace to calculate perturbations in planetary orbits. It provides a way to determine the effect of gravitational interactions on the motion of celestial bodies.
4. What is Laplace's role in the history of mathematics?
Laplace is considered one of the most influential mathematicians in history. His work in various areas, including probability theory, differential equations, and mathematical physics, laid the foundation for many later advancements in these fields.
5. How can students benefit from studying Laplace's contributions?
Studying Laplace's work can enhance students' understanding of advanced mathematical concepts and their applications in various scientific fields. It allows them to appreciate the historical development of mathematics and the significant impact it has on modern science.