Rosalind Franklin
Rosalind Franklin: The Unsung Hero of DNA
Rosalind Franklin: The Unsung Hero of DNAWhen we think of the discovery of the structure of DNA, we often associate it with the names James Watson and Francis Crick. However, there is another name that often goes unrecognized: Rosalind Franklin.
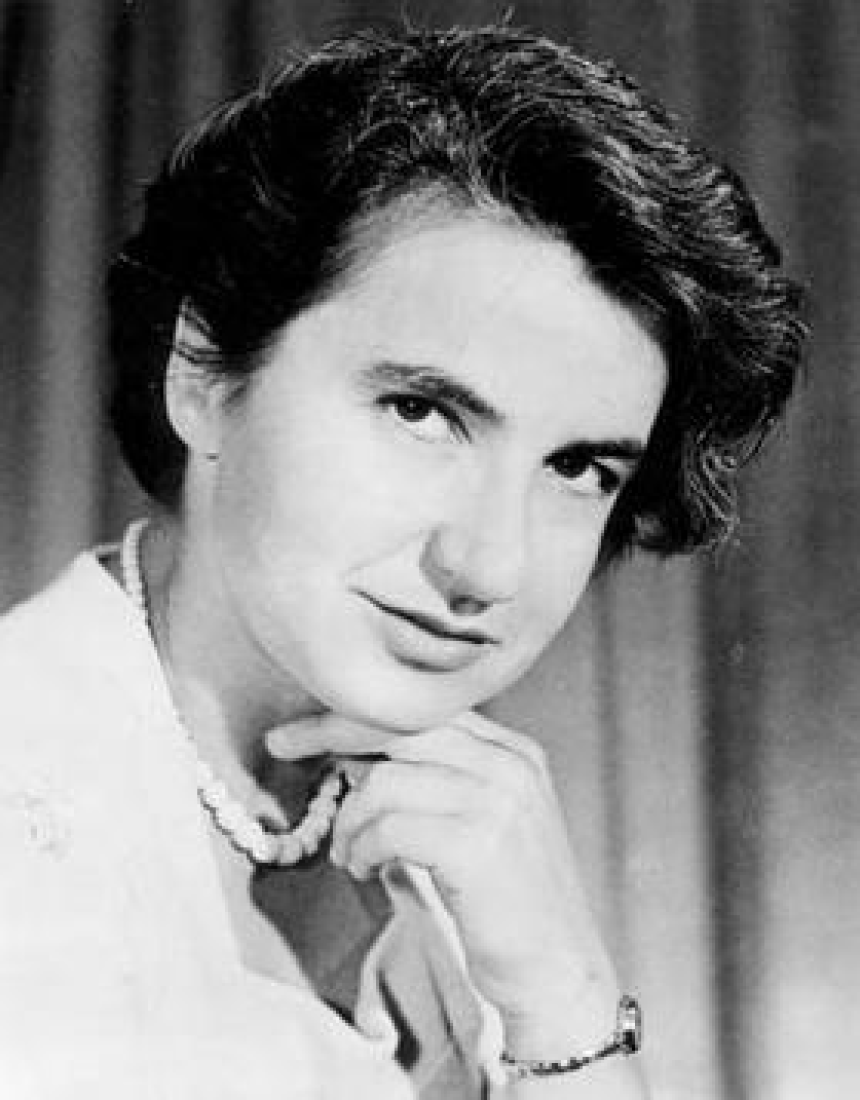
Who was Rosalind Franklin?Rosalind Franklin was a British scientist born in 1920. She specialized in X-ray crystallography, a technique used to determine the structure of crystals. Franklin made significant contributions to the field of molecular structure, particularly in the study of DNA and viruses.
Franklin's role in the discovery of DNA structureIn the early 1950s, Rosalind Franklin started working on DNA fibers at King's College in London. Her work involved obtaining high-resolution X-ray diffraction images of DNA fibers, which provided crucial evidence about its structure.
Franklin's most famous image, known as Photograph 51, played a crucial role in determining the structure of DNA. It showed a clear X-shaped pattern, indicating that DNA had a helical structure.
The controversy and recognitionUnfortunately, Franklin's contribution to the discovery of DNA structure was overshadowed by James Watson and Francis Crick's publication of their double helix model of DNA in 1953. It is important to note that Watson and Crick had access to Franklin's research and had seen her Photograph 51.
In 1962, Watson, Crick, and Franklin's colleagues Maurice Wilkins were awarded the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for the discovery of the structure of DNA. However, Franklin had passed away four years earlier and the Nobel Prize is not awarded posthumously.
Franklin's legacyDespite the lack of recognition during her lifetime, Rosalind Franklin's work has been widely acknowledged in the scientific community. Her research on DNA structure provided the foundation for future studies in molecular biology and genetics.
Today, Franklin is regarded as one of the most influential scientists of the 20th century. Her contributions to science continue to inspire new generations of researchers and her story serves as a reminder of the importance of acknowledging all contributors to scientific discoveries.
Frequently Asked Questions1. What is X-ray crystallography?X-ray crystallography is a technique used to determine the atomic and molecular structure of a crystal. It involves shining X-rays on a crystal and analyzing the pattern of diffraction produced.
2. What is Photograph 51?Photograph 51 is an X-ray diffraction image of DNA fibers taken by Rosalind Franklin in 1952. It provided crucial evidence for the helical structure of DNA.
3. Why is Rosalind Franklin often overlooked in the discovery of DNA structure?Rosalind Franklin's work was overshadowed by James Watson and Francis Crick's publication of the double helix model of DNA. Furthermore, Franklin passed away before the Nobel Prize was awarded, which further contributed to her lack of recognition.
4. What is Rosalind Franklin's impact on science?Rosalind Franklin's research on DNA structure laid the groundwork for future studies in molecular biology and genetics. Her work continues to inspire and shape scientific advancements in these fields.
5. What is the importance of recognizing Rosalind Franklin's contribution?Recognizing Rosalind Franklin's contribution to the discovery of DNA structure is important as it highlights the significance of giving credit where it is due. It also serves as a reminder that scientific breakthroughs are often the result of collaborative efforts and multiple researchers.