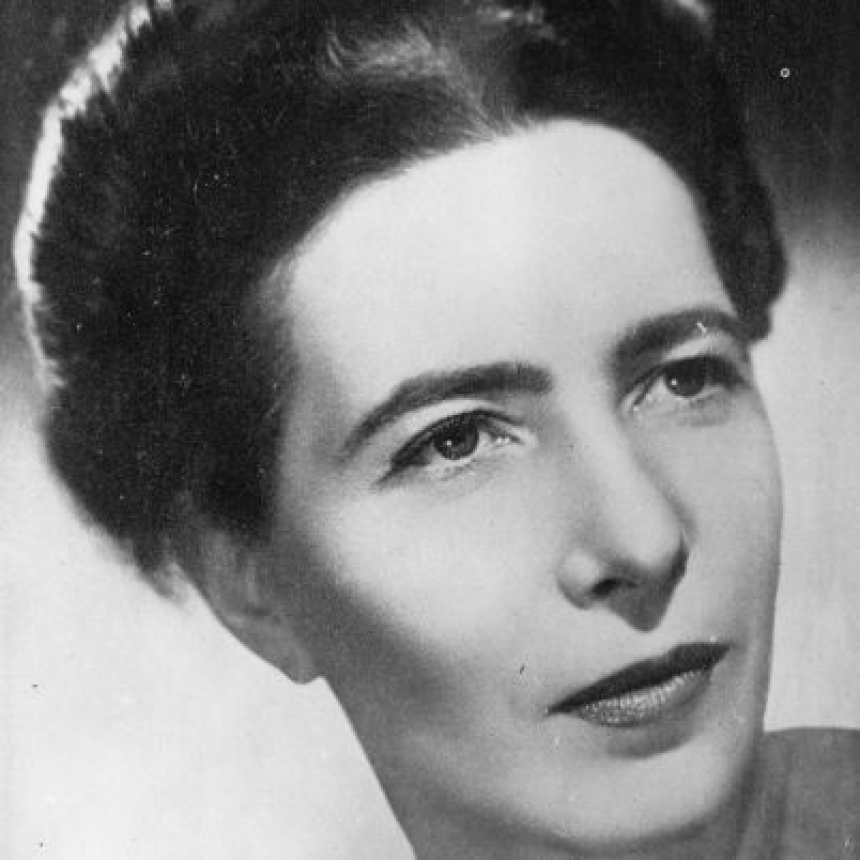
Sophie Germain
Sophie Germain: The Trailblazing Mathematician
Sophie Germain: The Trailblazing MathematicianSophie Germain was an incredible mathematician who made significant contributions to the field despite facing numerous obstacles due to her gender. Born on April 1, 1776, in Paris, France, Germain's passion for mathematics ignited when she was only 13 years old. Her love for numbers and problem-solving would lead her to become one of the most important figures in mathematics history.
Early Life and EducationGermain's journey into mathematics was anything but conventional. As a girl, she was not allowed to attend school or participate in the predominantly male academic circles that surrounded her. However, her thirst for knowledge could not be quenched, and she began studying mathematics on her own.
Germain was able to access her father's private library, where she came across books by some of the greatest mathematicians of her time. She immersed herself in the works of Leonhard Euler, Joseph-Louis Lagrange, and Carl Friedrich Gauss, teaching herself advanced mathematical concepts.
Sophie Germain and Number TheoryGermain's breakthrough in mathematics came when she discovered a math problem in Adrien-Marie Legendre's "Réflexions sur la théorie des nombres." While the problem was meant to be solved by male mathematicians, Germain took it upon herself to solve it anonymously.
After countless nights of intense calculations and research, Germain's solution reached Legendre, who was astounded by the quality of the work. He became determined to find out the identity of this brilliant mathematician named "M. LeBlanc."
Upon discovering that "M. LeBlanc" was, in fact, Sophie Germain, Legendre became her mentor and advocate. He introduced her to prominent mathematicians and secured her a position as a mathematician at the French Academy of Sciences.
Contributions to Elasticity TheoryAlthough Germain's accomplishments in number theory were groundbreaking, she made significant contributions to other areas of mathematics as well. She became interested in the field of elasticity theory, which deals with how materials deform under stress.
Germain's work in elasticity theory involved applying mathematical principles to understand the behavior of materials when subjected to strain. Her research played a crucial role in the development of engineering and structural design.
Legacy and RecognitionSophie Germain's contributions to mathematics did not receive widespread recognition during her lifetime. It was only after her death in 1831 that her work began to gain the recognition it deserved.
Germain's dedication to mathematics despite societal barriers paved the way for future generations of women in STEM fields. Her perseverance and determination continue to inspire young mathematicians and scientists today.
Today, Germain's legacy lives on through the Sophie Germain Prize, awarded biennially to mathematicians who have made significant contributions to number theory.
ConclusionSophie Germain's trailblazing journey in mathematics serves as a testament to the power of passion, determination, and resilience. Despite the limitations placed upon her due to her gender, she was able to overcome societal barriers and leave a lasting impact on the field of mathematics. Germain's story reminds us that brilliance knows no boundaries, and it is through the efforts of individuals like her that barriers are broken and new possibilities are created.
FAQs1. What were Sophie Germain's major contributions to mathematics?Sophie Germain made significant contributions to number theory and elasticity theory. Her breakthrough in number theory, where she solved a problem anonymously, led to her recognition by renowned mathematicians. Her work in elasticity theory played a crucial role in advancing structural design and engineering principles.
2. How did Sophie Germain overcome the limitations placed upon her due to her gender?Despite not being allowed to attend school or participate in academic circles, Germain self-taught herself mathematics by studying books in her father's private library. She faced numerous obstacles but persevered in her pursuit of knowledge, eventually gaining recognition for her work.
3. What is the Sophie Germain Prize?The Sophie Germain Prize is a prestigious award presented biennially to mathematicians who have made significant contributions to number theory. The prize is named in honor of Sophie Germain's groundbreaking work in the field.
4. How did Sophie Germain's work impact future generations of mathematicians and scientists?Germain's dedication to mathematics and her achievements despite societal barriers paved the way for future generations, especially women, in STEM fields. She serves as an inspiration for young mathematicians and scientists today and encourages them to pursue their passions despite any obstacles they may face.
5. Where can I learn more about Sophie Germain's life and work?There are several books and online resources available that delve into Sophie Germain's life and her contributions to mathematics. Some recommended reads include "The Woman Who Loved Math: The Improbable Life of Sophie Germain" by Joe Pappalardo and "Sophie Germain: An Essay in the History of the Theory of Elasticity" by Carl Gustav Hempel.