Werner Heisenberg
Werner Heisenberg and the Uncertainty Principle
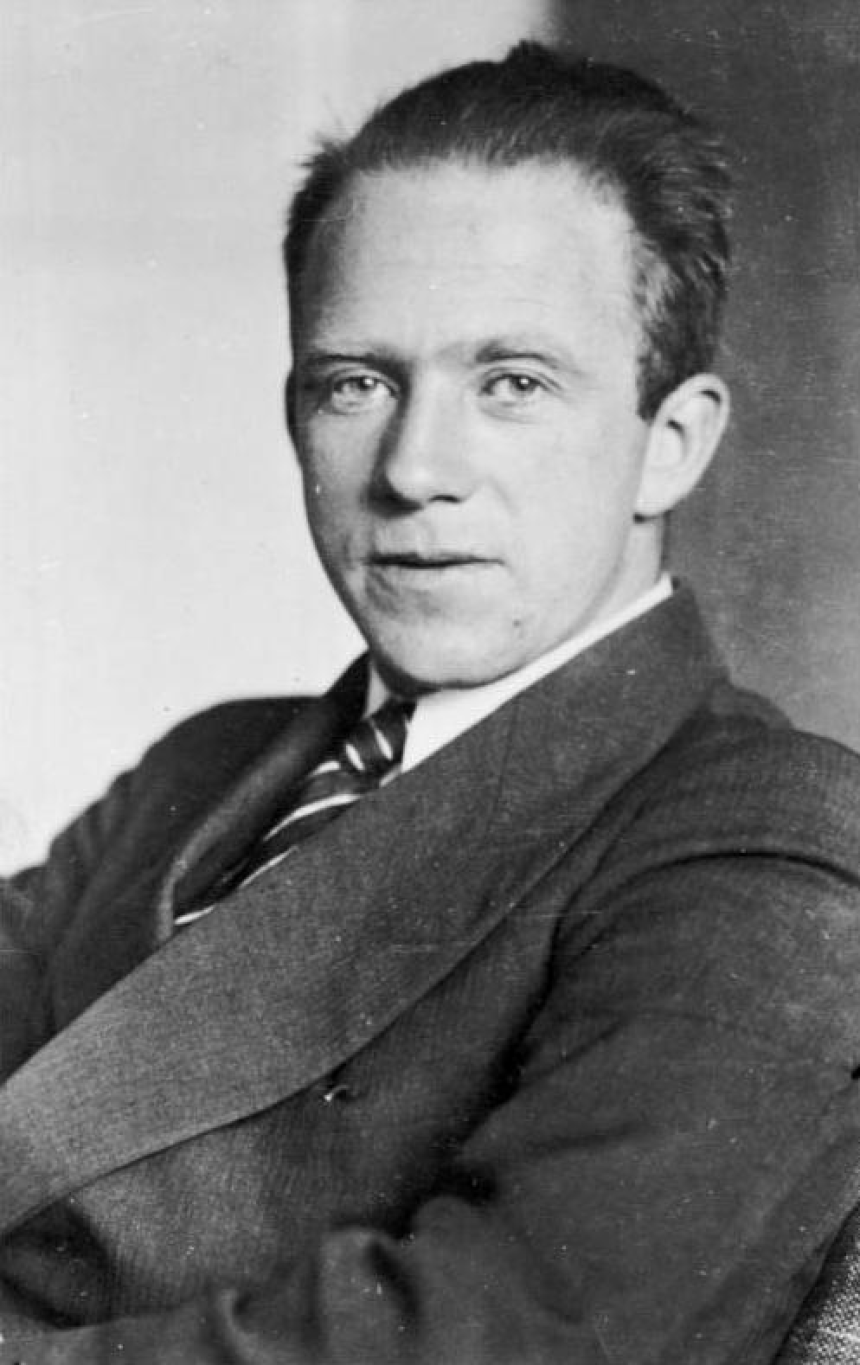
Werner Heisenberg and the Uncertainty PrincipleWerner Heisenberg, a German physicist, is renowned for his contribution to the development of quantum mechanics. Born on December 5, 1901, in Würzburg, Germany, Heisenberg's groundbreaking work on the uncertainty principle forever changed our understanding of the physical world.
Early Life and EducationHeisenberg came from an academic family, with his father being a professor of medieval and modern history. This environment fostered his interest in academia from a young age. Heisenberg pursued his studies in physics, mathematics, and philosophy at the University of Munich, where he earned his doctorate in 1923.
The Uncertainty PrincipleHeisenberg's most significant contribution to physics was the formulation of the uncertainty principle in 1927. This principle states that there is an inherent limit to the precision with which certain pairs of physical properties of a particle can be known simultaneously. It challenged the Newtonian idea that the position and momentum of a particle could be determined exactly.
The uncertainty principle revolutionized our understanding of the microscopic world. It showed that the act of observing something at the quantum level affects its behavior, making it impossible to know both the position and momentum of a particle with absolute certainty. This principle has profound implications for various scientific fields, including quantum mechanics, atomic physics, and even cosmology.
Heisenberg's Other ContributionsBesides the uncertainty principle, Heisenberg made several other significant contributions to physics. He formulated the matrix mechanics formulation of quantum mechanics, alongside Max Born and Pascual Jordan, which provided a mathematical framework for describing quantum systems using matrices. This paved the way for the development of quantum field theory and quantum electrodynamics.
Moreover, Heisenberg played a crucial role in the German nuclear energy project during World War II, known as the Uranium Club. Although the project did not successfully produce the atomic bomb, Heisenberg's efforts helped lay the foundation for nuclear technology.
Awards and LegacyHeisenberg's contributions to the field of physics were recognized with numerous accolades. In 1932, he received the Nobel Prize in Physics "for the creation of quantum mechanics, the application of which has, inter alia, led to the discovery of the allotropic forms of hydrogen."
Heisenberg's work continues to inspire scientists and students alike. His ideas and principles provide a deep understanding of the fundamental nature of matter and have shaped the development of modern physics. The uncertainty principle, in particular, remains a cornerstone of quantum mechanics and a testament to Heisenberg's intellectual genius.
ConclusionWerner Heisenberg's groundbreaking discoveries and contributions to physics, most notably the uncertainty principle, have profoundly impacted our understanding of the physical world. His work continues to be celebrated today and serves as an inspiration to future generations of scientists.
Frequently Asked Questions about Werner Heisenberg:1. Who was Werner Heisenberg?
Werner Heisenberg was a German physicist known for his work on the uncertainty principle and his contributions to quantum mechanics.
2. What is the uncertainty principle?
The uncertainty principle, formulated by Heisenberg in 1927, states that there is a limit to the precision with which pairs of physical properties of a particle can be known simultaneously.
3. How did Heisenberg contribute to the development of quantum mechanics?
Heisenberg, along with Max Born and Pascual Jordan, formulated the matrix mechanics formulation of quantum mechanics. He also made significant contributions to nuclear physics and played a role in the German nuclear energy project during World War II.
4. How did Heisenberg's work impact the scientific community?
Heisenberg's work revolutionized our understanding of the microscopic world and laid the groundwork for quantum mechanics. His ideas and principles continue to be influential in the field of physics.
5. What awards did Heisenberg receive?
Heisenberg was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1932 "for the creation of quantum mechanics."